
In 2022, 14.7% of employees in the EU were low-wage earners, against 16.2% in 2018. Low-wage earners are employees earning two-thirds or less of the median gross hourly earnings in the country of work.
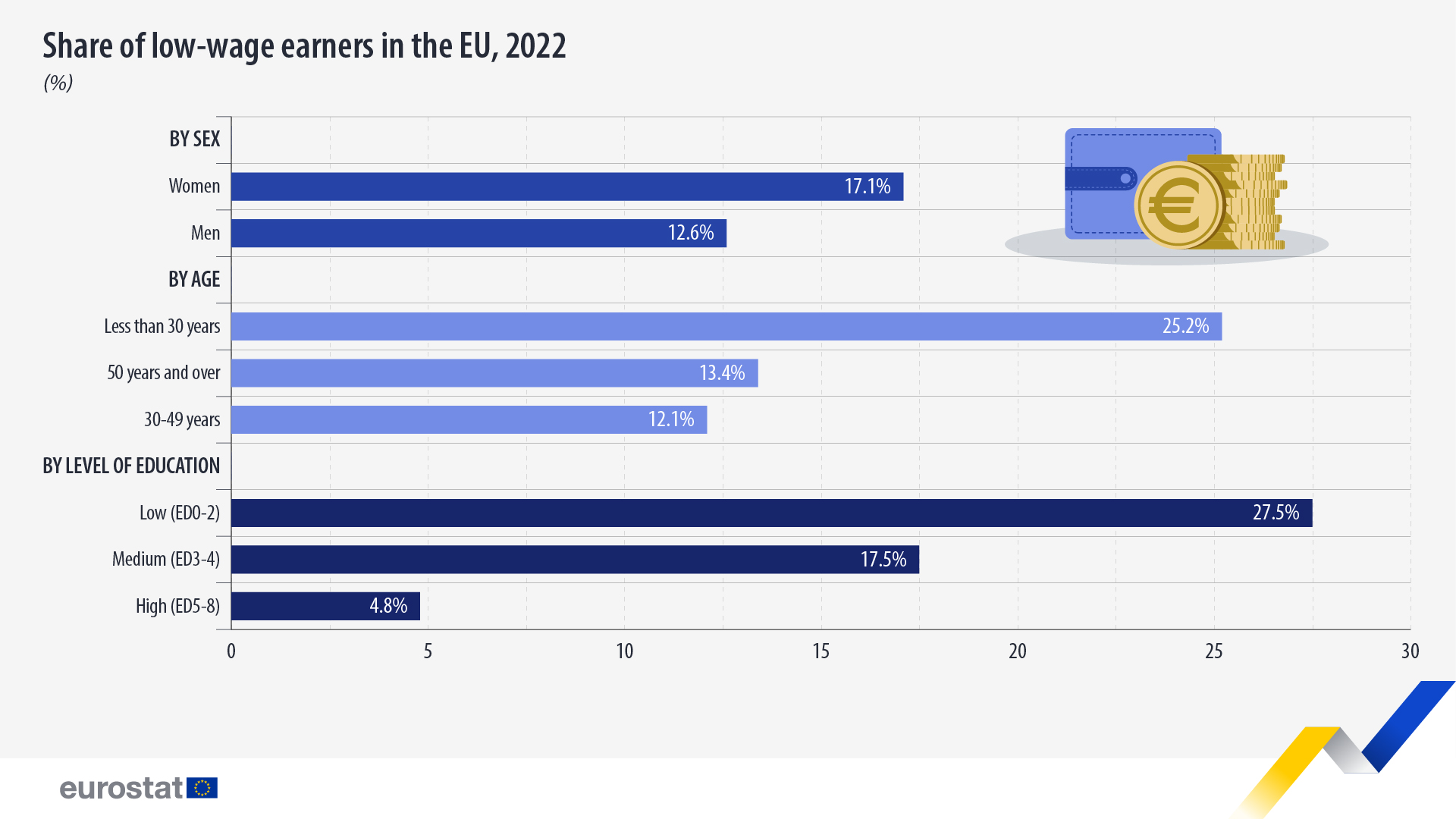
The share of low-wage earners was higher among women than men in 2022 (17.1% compared with 12.6%). In 2018 the shares were 18.2% of female and 12.5% of male employees.
Low-wage earners accounted for about a quarter (25.2%) of employees younger than 30. In the older age groups this share was lower: 12.1% among employees aged 30-49, and 13.4% among those older than 50.
Source datasets: earn_ses_pub1s, earn_ses_pub1a and earn_ses_pub1i
The lower the level of a person’s education, the higher the likelihood of being a low-wage earner. In 2022, 27.5% of employees in the EU with a low education level were low-wage earners, compared with 17.5% of employees with a medium level of education and 4.8% of those with a high education level.
The proportion of low-wage earners varied significantly among EU countries in 2022. The highest share was observed in Bulgaria (26.8%), followed by Romania (23.9%), Latvia (23.3%), Greece (21.7%), Estonia (21.2%) and Cyprus (20.0%).
In contrast, less than 10% of employees were low-wage earners in Portugal (1.8%), Sweden (4.1%), Finland (6.5%), Italy (8.8%), Slovenia (9.4%) and France and Denmark (9.7% both).

Source dataset: earn_ses_pub1s
In 2022, the share of low-wage earners recorded in the EU was highest in accommodation and food service activities (35.1%); followed by administrative and support service activities (32.3%), that includes the persons employed by interim agencies.
The type of contract also plays a role: among employees with an employment contract of limited duration, 27.2% were low-wage earners, compared with 12.6% of those with an indefinite contract.
Source: Eurostat, https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/product?code=ddn-20250227-1